WP Super Cache is a page caching plugin built by the Automattic team. It is a free extension and has over two million active users. W3TC is another widely used caching plugin. Like WPSC, it is very popular and has hundreds of thousands of users. Below, we’ve compared the options and features of these two extensions.
Ease of use
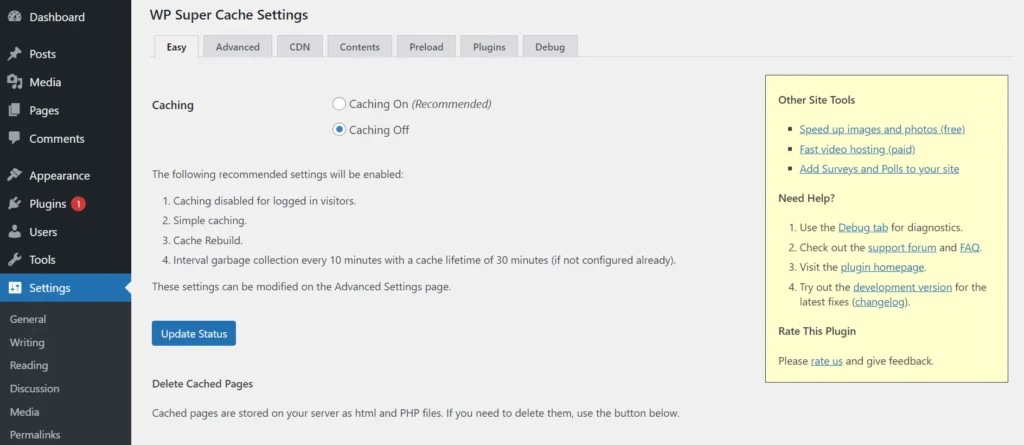
WP Super Cache is super easy to set up. It shows two radio buttons in the Easy settings tab – Caching On and Off. To enable caching on your WordPress site, all you have to do is select the “On” radio button and click the Update Status button.
The Advanced settings of WPSC give users more control. Here are the settings you will find in the Advanced section of WPSC:
- Enable compression of pages.
- Disable for logged-in visitors.
- Enable for every visitor of the site.
- Prevent for users who have set a cookie on their browsers.
- Refresh the page when someone posts a comment.
- Delete all pages/posts that are cached when an author or admin publishes a new page/post.
W3TC has too many options. While enabling page caching, you can choose one of these two caching methods – disk and disk enhanced. Similarly, while enabling minification of JS/CSS files, you can choose the HTML, JS, and CSS minifier you want the plugin to use. Thus, configuring this extension is a bit tricky and time-consuming.
Features comparison
You can configure WPSC and W3TC to preload the pages of the site at the time of your choice. When you enable this function, the plugins will delete their existing cache and cache all website pages without killing your server.
W3TC can minify JavaScript and Cascading Stylesheet files and combine them to reduce HTTP requests. It can also minify the HTML code of a WP page. WPSC users will have to find and install a WP extension that will minify files on their websites, as it can’t minify files by itself.
Configuring CDN on WP sites can be tricky. The two plugins support integration with CDNs. To set up CDN on sites powered by either of these extensions, open its CDN settings page and fill in the form the page displays.
Although the Database caching function is useless as MySQL uses the highly efficient InnoDB database engine by default and InnoDB employs the InnoDB buffer pool, the W3TC lets you activate database caching. When you enable DB cache, W3TC will cache SQL queries of the user’s choice and allow users to set an expiration time for the same. WPSC doesn’t come with the Database caching feature.
W3TC’s latest feature is its ability to create WebP files automatically. To activate this feature, you must enable its Image Service module from the “Feature Showcase” page of the plugin. WPSC doesn’t generate WebP files.
W3 Total Cache allows users to set an expiration time for CSS, JS, and media files. WPSC doesn’t have the option to set the same.
Which plugin is better?
WPSC might not have too many functions, but it is the most straightforward caching plugin. You have to click a checkbox and a button to activate caching on your site. If you have not installed several WordPress extensions and your theme is blazing fast and doesn’t have too many customization options, WPSC is the best plugin you can use. If you’re using several extensions and your theme has many options, and the page speed score of your site is poor, WPSC won’t help you (This is from my personal experience).
W3TC comes with four functions – minification, and page/database/object caching but configuring it can be a headache. It can break the site even when you don’t modify the settings. It has some functions which are difficult to understand. If you configure the plugin properly after spending a lot of time understanding and testing the features, W3 Total Cache can boost the site’s page speed score.
Alternatives
WP Rocket is the best alternative to the two caching plugins we’ve covered on this page. Almost 2 million users use it. WP Rocket supports every feature WPSC and W3TC offer and is easy to configure. WP Rocket also comes with features that you won’t find in any of the free caching extensions that you might be aware of. The features we’re talking about are critical CSS generation, reducing WP Heartbeat activity, optimizing Google Font files, and more.

